The Duodopa Pump
The system consists of four parts:
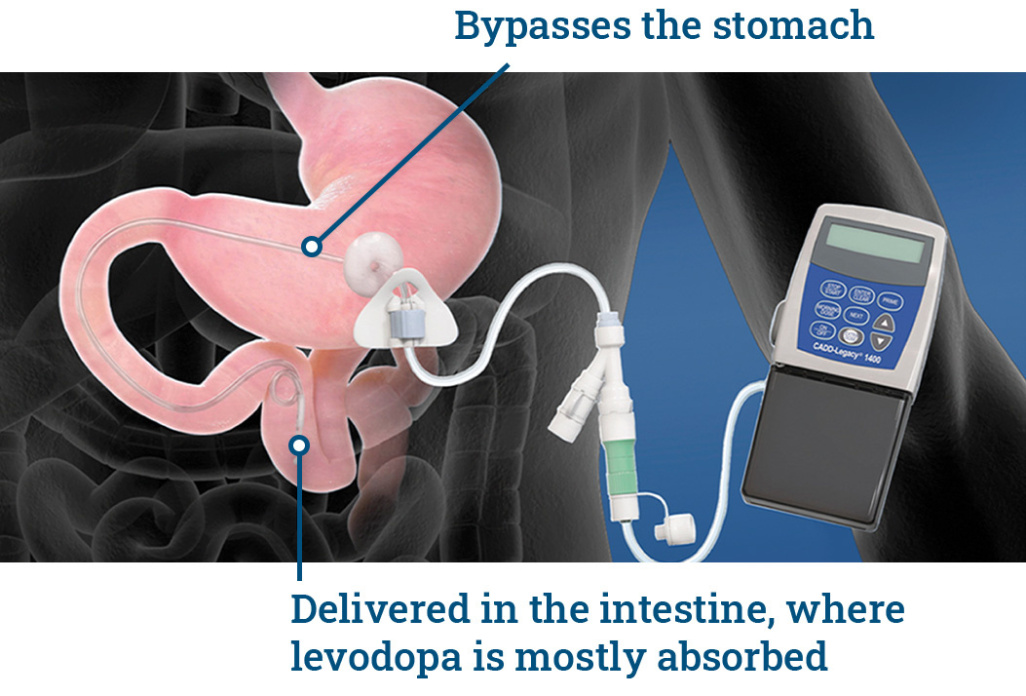
External PEG tube. (Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Tube) A tube that leads from the pump through the abdominal wall and into the stomach.
Internal J tube. (Jejunostomy Tube) A tube that is placed within the PEG tube through the stomach and into the small intestine, delivering Duodopa.
CADD-pump. (Computerised Ambulatory Delivery Device) The pump administers Duodopa continuously into the small intestine. The continuous and direct administration into the small intestine contributes to providing a more constant amount of Levodopa into the body through the day.
Medication cassette. A plastic container that holds the Duodopa Gel. This is connected to the pump and contains the equivalent of 20 tablets of 100mg Levodopa (2000mg total) and 25mg Carbidopa (500mg total). The cassette must be stored in the fridge and should be changed once a day (rarely twice).
The flow rate and dosage amount is programmed into the pump by a doctor or Duodopa nurse specialist.
The cassette is connected to the pump and the pump is connected to the gastro- jejunostomy tube (called a PEG-J tube) which is placed into the gut (small intestine).
The gel is administered throughout the waking day (15 to 16 hours) via the pump connected in the morning and disconnected in the evening at bedtime.
The pump is taken off for showering and at night for sleeping.
Medication kick in time in the mornings is usually around 10 – 15 minutes.
The Pump has three delivery settings – a Morning Dose, a Continuous Dose and an on demand Bolus Dose.
The total dose per day of Duodopa is composed of these three individually adjusted doses They can be adjusted via the pump settings.
Once the pump is started, a larger dose is given in the morning to quickly reach the correct amount of medication needed, followed by a continuous delivery of medication throughout the day until bedtime
In detail, these doses are:
Morning dose: The morning dose is an individualised daily loading dose administered for between 10 and 30 minutes to quickly reach the correct amount of medication needed.
Continuous maintenance dose: The Continuous Maintenance Dose (CMD) begins automatically after the Morning Dose and continues for the remainder of the 16-hour infusion period.
This means that the level of the medication in the blood stays similar.
The dose is adjusted to maximise the functional “On” time during the day by minimising the number and duration of “Off” episodes (bradykinesia) and minimising “On” time with disabling dyskinesia
Additional bolus doses may be administered as required. In detail this dose is:
Extra bolus doses: Extra doses of Duodopa are used to address immediate medical needs, such as the rapid deterioration of motor function. There is normally a lock out time to prevent overdosing with extras doses.
If the need for the extra dose feature exceeds five per day, then the continuous maintenance dose should probably be increased.
All the settings are adjustable. However, pump settings are usually locked either fully or partially and are then adjusted by a Neurologist or Parkinson’s Nurse as part of the Duodopa delivery for the symptom management process.
In our case, we have an unlocked Pump and adjust the pump settings ourselves in response to symptoms that manifest themselves.
The medicine cassettes are for single use only and should not be administered for longer than 16 hours even if some medicinal product remains.
Treatment with Duodopa using a permanent tube can be discontinued at any time by withdrawing the tube and letting the wound heal.
Treatment would then continue with oral medication including levodopa/carbidopa.
Back to main site: https://adamsonstradley.com